Erik Sundin
Professor of Sustainable Manufacturing


Project time: 2018 – 2021
Budget: 9 206 325 kronor
Funding: SIP Produktion2030
The aim of the ARR project is to develop the potential of automation in repairs and remanufacturing
Remanufacturing is an industrial process where used products are being restored to a quality which is the same or even better than newly produced products. The ARR project has the objective to develop the potential for automation in repair and remanufacturing. The goals here are to identify the challenges with automation of repairs and remanufacturing and to demonstrate conceptual implementations. The motives for the participating companies in the project is that they see potential of automation solutions to achieve a higher production efficiency as well as improved work environment. The work environment can be improved by avoiding interaction with hazardous materials or by performing heavy lifting in disassembly and cleaning. Within this project we will start by performing detailed automation analyses at four repair and remanufacturing SMEs, developing and implementing virtual and physical demonstrators for the specific company needs and at the same time share this knowledge with industry, especially SMEs. Along the project we will also conduct sustainability assessment to make sure that the automation solutions that we are developing are sustainable from economic, ecologic and social perspectives. The participating partners are: Linköping University (researchers), Swerea IVF (researchers), Yaskawa Nordic (robot-system integrators), Scandi-Toner (toner cartridge remanufacturer), Scandi-Gruppen (photocopymachine repairer), Inrego (computer remanufacturer) and Megalans (electric car component remanufacturer).
The project aims at radically improving the working environment and the employee security within the heavy manufacturing industries by using and adapting the latest technology for low and ultraprecise positioning and decision support systems. The target is to increase security and safety by adapting the decision-support and positioning system for the heavy manufacturing industries.
2017 – 2018
Maintenance in existing plants is becoming increasingly important, where predictive maintenance has become an emerging technology. The use of decision support tools contributes to environmentally and economically sustainable production. Within this project, different types of digital twins have been designed and evaluated. Specifically, new predictive model types have been tested in two different industrial case studies; a heat exchanger at SSAB and a profiled header at Svenska Fönster AB.
2017 – 2018
A research collaboration between Luleå University of Technology and the company RGS 90 will provide new treatment methods for three common but problematic types of waste.
2015 – 2019

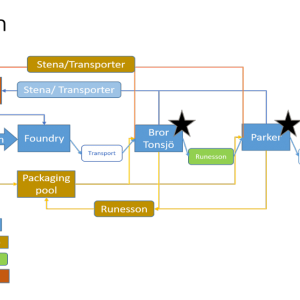
SCARCE II will develop a demonstrator to show how SMEs and associated value flows can increase efficiency, competitiveness, sustainability and internal collaboration through digitalisation. The goal is to show the value of a new digital solution. SCARCE focuses on two subcontractors in the value chain linked to Scania and Volvo. The demonstrator is a cloud-based solution that connects three test beds in the industry; Stena Industry Innovation Lab, Chalmers, RISE IVF lab, Mölndal and KTH's test bed in Södertälje with the help of Siemens, AFRY, Qbim, Virtual Manufacturing and EQPack.
2020 – 2022
Digi-load focuses on to enhance the competitiveness in the Swedish surface treatment industry through automation and digitalization
2017 – 2020
Knowledge is needed that can support design and control of automation in material handling systems.
2019 – 2022
To demonstrate the new technology with robots that enable Swedish companies to develop innovative new products for automated production o maintenance.
2017 – 2020
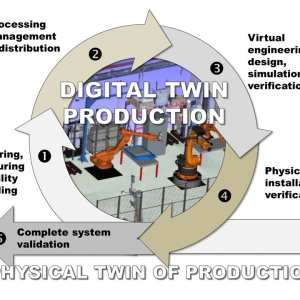
Methods for 3D scanned digital twins for efficient development and installation of production facilities at SMEs
2018 – 2021
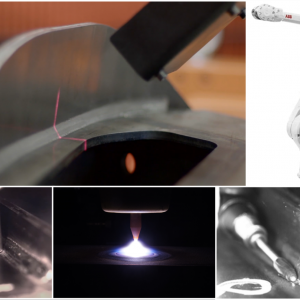
MIDWEST will develop mechanisation solutions for Post-weld treatment methods of welded components.
2020 – 2023
The project's goal is to assist industry enabling sustainable work for operators during assembly of wire harnesses.
2022 – 2025

SE:Kond2Life - Ecosystem for reuse of automotive components
2019 – 2022