Project time: 2019 – 2022
Budget: 7 200 000 kronor
Funding: SIP Produktion2030
The goal is to demonstrate the additive manufacturing of micrometer/millimeter wave components.
Next generation of micrometer/millimeter wave components for future mobile communication would benefit significantly from further flexibility in product design. Through additive manufacturing (AM), flexible production could be realized that would allow a future digital product platform for such product design. The AM technology has so far not been addressed for this kind of applications, but would if successful mean a significant breakthrough in product realization. Owing to product specifications, mass customization could be combined with mass production with AM, which is not typical for AM. The basis for this potential future implementation is the combination of Cu-base materials solution and as near precision manufacture by AM as possible, where the powder-bed technologies laser powder bed fusion and binder jetting will be applied. The project is a co-operative effort involving Ericsson as end-user and problem owner, Chalmers and RISE IVF as research providers and EOS and Digital Metal as core technology providers in AM. At project, the expected outcome is strengthened industrial ability in developing manufacturing to match future products through: A digital chain from product modelling to design for AM to product realization; proof-of-concept for applying AM to generate micrometer and millimeter wave components for future 5G systems; provision of Cu-base material solutions for laser powder bed fusion and binder jetting for intended future applications.
Vinnova dnr: 2019-00786
DiLAM strengthens the competitiveness of the Swedish manufacturing industry by aligning the digital and physical supply chains for additive manufacturing of large parts.
2017 – 2020
Reduced lead times and improved performance for tooling through innovative manufacturing and assembly strategies as well as optimised design enabled by use of additive manufacturing (AM).
2016 – 2018
DIDAM develops and demonstrates digitalization solutions to industrialize Additive Manufacturing
2020 – 2023

The project aims to test the idea of an effective circulation system for material waste from additive manufacturing. Our goal is to map the prerequisites for closer collaboration between material suppliers and additive manufacturers, including new business models, partnerships and logistics solutions.
2017 – 2018
The overall goal of DiSAM is to create a unique test AM Hub in Sweden for metal and polymer based additive manufacturing processes.
2017 – 2021
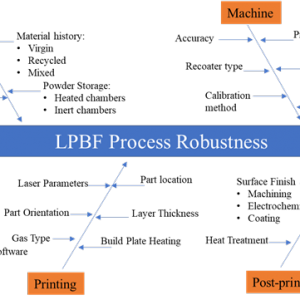
Assessing the Robustness of the Laser Powder Bed Fusion Process
2021 – 2024
The aim of the project is to demonstrate utilization of additive manufacturing for copper-based products and process solutions and faster adaption
2016 – 2018

Powder metallurgy is an attractive, alternative method to manufacture large components for nuclear power plants.
2021 – 2024

Design process from concept to printable stl-file for AM including surface based networks in the structure.
2019 – 2022
The project's main goal is to develop a design and manufacturing methodology, for resource efficient additive manufacturing of components in the automotive industry.
2017 – 2020
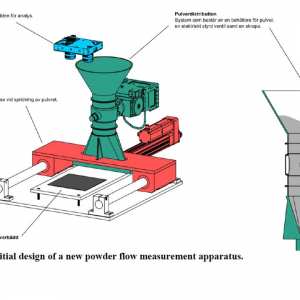
This project intends to design and develop a new test methodology for evaluation of power flowability in powder bed fusion (PBF) systems. The test apparatus will simulate powder flow in PBF machines and can be used for optimizing the powder layering behavior for potential utilization of alternative powder qualities. Additionally, this equipment creates opportunities for both powder producers and AM part manufacturers to minimize powder waste and maximize material utilization.
2017 – 2018
IDAG aim to identify gaps and propose actions for the digital infrastructure necessary to industrialize additive manufacturing technologies. Actors from a new type of value chain of manufacturing companies – from powder to product – collaborate with digital solution providers and researchers to understand the needs and articulate the necessary actions through analysis of industrial cases. The target is to deliver a description in the form of a roadmap for how these actions can be developed and provided in order to ensure flexible and scalable digital platforms for additive manufacturing value chains.
2019 – 2019