Project time: 2018 – 2020
Budget: 5 410 000 kronor
Funding: SIP Produktion2030
Method to understand how to automate information handling to get more efficient handling of production deviations.
Objectives
Production and logistics are highly complex due to dependencies among many interacting systems, dynamics, and frequent changes. A consequence is frequent deviations from production plan despite systematic work to increase process stability. The project is aimed at supporting the handling of deviations and re-scheduling of tasks by solutions that automate relevant information flows and processes. The project develops a model framework that identifies and describes needs for support, information and automation, and a methodology that guides companies to specify their needs.
Impact and Results
Competitiveness is expected to increase as result of more automated and efficient handling of deviations within production. The expected impact from implementing such information automation is faster reaction and flexibility to deviations and changes of production plans, as well as reduced propagated effects. The methodology can give companies a good base for future investments that employ technological solutions, thereby increasing automation use. Furthermore, increased automation will give access to relevant information and increase knowledge of events.
Approach
Framework and methodology is formed by experiences from case studies in industrial partner companies, which cover different needs and aspects. The intention is to enhance the state-of-art and provide important solutions for increased digitalization and information automation. A crucial part of the project is the knowledge dissemination of solutions to Swedish industry, especially SMEs. The 30-month project is lead by Swerea IVF together with Chalmers Univ. of Techn., Royal Inst. of Techn., Brogren Industries, Federal-Mogul, Volvo Penta, Tyri Lights, and Marcus Komponenter.
Reduce the environmental impact of foundries by reducing the amount of sand waste using machine learning.
2023 – 2024

Tidsättning av manuell montering är centralt för verkstadsindustrins konkurrenskraft.
2021 – 2024

The project will develop a concept for production workers to easily build simple low-cost IoT-aided improvement solutions at the production shop floor.
2018 – 2020
The project aims to use deviation data for improving the product design and production.
2020 – 2023
This project aims to contribute to the development of future ERP-systems. The project will explore how to offer work, redefine work roles and challenge companies to make use of advanced systems support and the technology within and around these. Overall, the project aims to contribute to the development of both the next generation of ERP-systems and a complementary change in the way firms see upon work organization, so that technology can support and meet the needs of the humans within organisations rather than enforcing structures upon them.
2019 – 2019
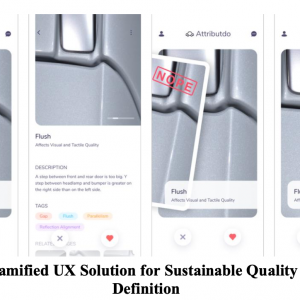
Two major disruptive trends – electrification and digitalization are changing customer preferences, leading to the probably most substantial transformation in the automotive industry we observed in decades. Finding a balance between customer’s requirements towards “zero-emission vehicle,” “connected car,” choice of materials, clarity of functions, and interface modes under the pressure of production time and cost are not easy. The AttributDo-project aims to help engineers create, define, verify and validate new and existing design features for new product development.
2021 – 2021
DIDAM develops and demonstrates digitalization solutions to industrialize Additive Manufacturing
2020 – 2023

The overall goal of DiSAM is to create a unique test AM Hub in Sweden for metal and polymer based additive manufacturing processes.
2017 – 2021
The project aims to reduce the lead time for sheet metal die tryout by optimizing the value stream and develop methods for numerical compensation of die and press deflections.
2017 – 2019
Novel methods, techniques and software for simulation of electrodeposition and galvanization processes.
2020 – 2023
DiVISI aims at investigating how sharing of digital information can improve the forest-forest industry value chain.
2020 – 2023
The project aims a digitising the temperatures during the casting of rolls and suggest actions to the casting manager to reduce the variability of the process
2015 – 2016
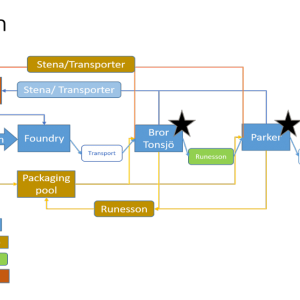
SCARCE II will develop a demonstrator to show how SMEs and associated value flows can increase efficiency, competitiveness, sustainability and internal collaboration through digitalisation. The goal is to show the value of a new digital solution. SCARCE focuses on two subcontractors in the value chain linked to Scania and Volvo. The demonstrator is a cloud-based solution that connects three test beds in the industry; Stena Industry Innovation Lab, Chalmers, RISE IVF lab, Mölndal and KTH's test bed in Södertälje with the help of Siemens, AFRY, Qbim, Virtual Manufacturing and EQPack.
2020 – 2022
Developing circular production systems using digital technologies
2021 – 2024

The project aims to digitalize established tools for production disturbance handling.
2018 – 2020
The project aims at facilitating the implementation of Smart Maintenance through extended collaboration within the maintenance community.
2017 – 2019
The paintshop is often a bottleneck in production and the processes are fine-tuned based on testing on numerous prototypes. To meet the future demands there is a great need to improve the product preparation process. The aim is to develop methods, techniques and software, and supporting measurement methodology, for simulation of paint curing in IR and convective ovens. The goal is to assist the industry to further develop and optimize their surface treatment to be more energy and cost efficient; to have a shorter lead time in product development; and to give a higher product quality.
2016 – 2019

SCARCE will investigate the needs, possibilities and obstacles in value chains up- and down-stream from a focal SME company. SCARCE will explore what data to measure and visualize, and how this data can enable more automated execution, as well as, more dynamic and proactive planning of production capacity and material flows across the companies in the value chain. In addition, we will study organizational capabilities, especially the future human role, for implementing and managing in a digital and data-driven value chain.
2019 – 2019
Målet var att förstå de utmaningar som den svenska och japanska industrin står inför studiebesök.
2017 – 2018

To demonstrate the new technology with robots that enable Swedish companies to develop innovative new products for automated production o maintenance.
2017 – 2020
WELDVISI will create a new sensor-based assistance system for manual manufacturing with real-time cognitive feedback and documentation of parameters.
2022 – 2025
The project aims at radically improving the working environment and the employee security within the heavy manufacturing industries by using and adapting the latest technology for low and ultraprecise positioning and decision support systems. The target is to increase security and safety by adapting the decision-support and positioning system for the heavy manufacturing industries.
2017 – 2018
DiLAM strengthens the competitiveness of the Swedish manufacturing industry by aligning the digital and physical supply chains for additive manufacturing of large parts.
2017 – 2020
Improve the efficiency of sawmills, including improved monitoring and maintenance of the production line. This by sharing data via digital twin between the actors in the maintenance chain.
2019 – 2019