Project time: 2020 – 2023
The project will create a digital tool for solving the largest issue in multi-material design: the Δα-issue.
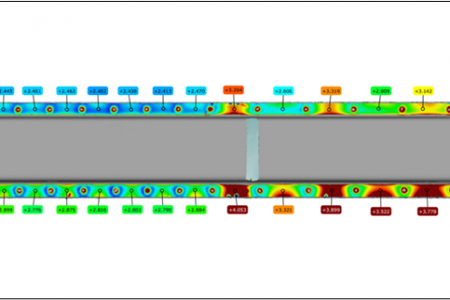
This project will enable a prediction tool to handle the largest obstacle for multi-material design: “the Δα-problem”. There is a large need for a flexible digital tool for prediction of deformations, adhesion, and fracture in adhesively bonded multi-material components and in manufacturing of epoxy-based composites. Adhesive bonding is a commonly used method for joining of multi-material components, often in combination with mechanical joining methods, such as friction elements or rivets. One large issue regarding adhesive bonding of multi-material components is the deformations caused by the different thermal expansion in the used materials. These deformations lead to poor adhesion, and in some cases also fracture, between the adhesive and the materials. Earlier work has shown that the amplitude of the deformation is dependent on several factors, such as the distance between fasteners, the thickness of the adhesive and the thicknesses of the materials. However, there is no available tool for prediction of the impact of the deformations on the adhesion. This project will develop a model for prediction of the deformations and their impact on the quality and fracture risk of the adhesively bonded joint. This will increase the possibility to design multi-material components in accordance with the light-weight strategy “right material at the right place” and thereby enable further reduction of component weight and increased safety and efficiency in design, production planning and manufacturing of new products.
Hybrid joints, combination of gluing and mechanical joining are highly demanded where several materials are to be used and assembled. HJT therefore focuses on the smart factory's ability to create flexible production with simulation and programming in a digital twin that combines the latest technology for bonding, assembly and mechanical joining, rheology based simulation and automated collision-free planning. The projects goal is to focus on the whole hybrid joining process and to establish a testbed for hybrid joining as a resource for Swedish Industry.
2017 – 2020
Difficulties in joining are often a limiting factor for vehicle manufacturers during product weight reduction.
2020 – 2023

To lay the foundation for tomorrow’s network of circular economy microfactories producing products designed by Swedish industry and produced from local recycled plastics.
2022 – 2023

New designs for fuel cell plates can be introduced faster and cheaper using efficient modeling technology
2021 – 2024